Sorry, your data is currently unavailable

- What is data availability?
- What is a data availability layer?
- Interesting data availability layers
- The future of data availability
What is data availability?
In digital assets, data availability ensures that all network participants have the required transaction data to verify blocks, thereby preserving the network’s integrity and trust. As the market expanded with more users interacting with different networks, the volume of blockchain data, including transaction details, block information, and the ledger’s state, grew significantly.
Data availability is vital because participants need access to historical data whenever a new block is created or verified. Problems arise when developers attempt to scale the network. As it expands, nodes are required to store and process increasing amounts of data, leading to bottlenecks.
To tackle the challenges of data availability and scalability, which depend on a single blockchain for all processes, new specialized data availability solutions are being developed. These solutions provide better overall performance and reduce gas costs.
What is a data availability layer?
A data availability layer is a storage solution designed to handle large volumes of data, which can be managed either on-chain or off-chain. It separates the responsibility of data availability from other blockchain functions such as execution and consensus.
In systems utilizing a data availability layer, the blockchain's data is stored independently from the main chain. This layer ensures the reliable storage of data and provides access to nodes when validation is required.
Common techniques employed in a data availability layer include erasure coding, data sharding, and other forms of data partitioning.
Interesting data availability layers
As the demand for scalability grows, data availability protocols have been becoming increasingly popular:
- Near DA
The data availability layer of Near Protocol uses sharding, a technique that separates the blockchain into small fragments AKA shards. Near can achieve significant scalability as it can readily reshard and scale in response to increasing demand, thus maintaining a consistently ample and cost-effective data availability solution.
- Celestia
Celestia has introduced an innovative concept known as Data Availability Sampling. DAS allows nodes to verify the availability of data without needing to download the entire dataset. Nodes can randomly sample small portions of the data to ensure that the entire block is available, which significantly reduces the bandwidth and storage requirements for nodes.
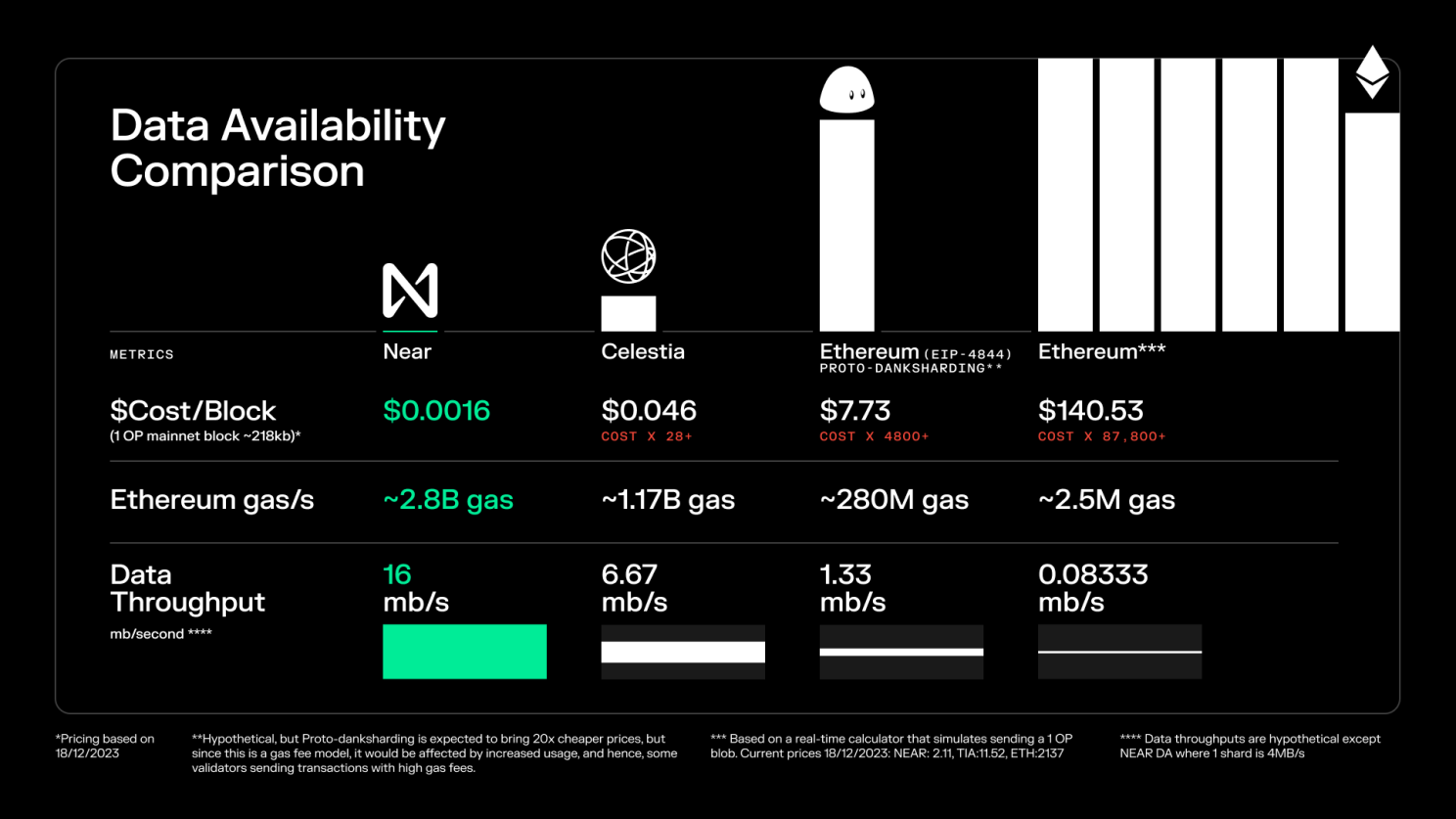
The future of data availability
With the digital assets market continuing to grow, data availability will become an increasingly important topic. With more data being stored and processed, blockchains and applications must be able to retrieve this data to execute interactions. Although the topic is quite difficult for the average user, we do see interesting opportunities in these protocols. Some of these projects already experienced some upward momentum in 2024 and we expect that there will be more opportunities in the future. However, it's still early to determine if we have a winner yet.